Help: How to use Wiki-MPM
Protein-protein interactions of your interest can be searched from any page by using the search form on the top right of the page, as shown below. You can search interactions based on:
- gene symbols (e.g. "EGFR")
- associated GO terms (e.g. "Epinephrine Transport")
- associated pathways (e.g. "hemostasis")
- associated diseases (e.g. "cancer")
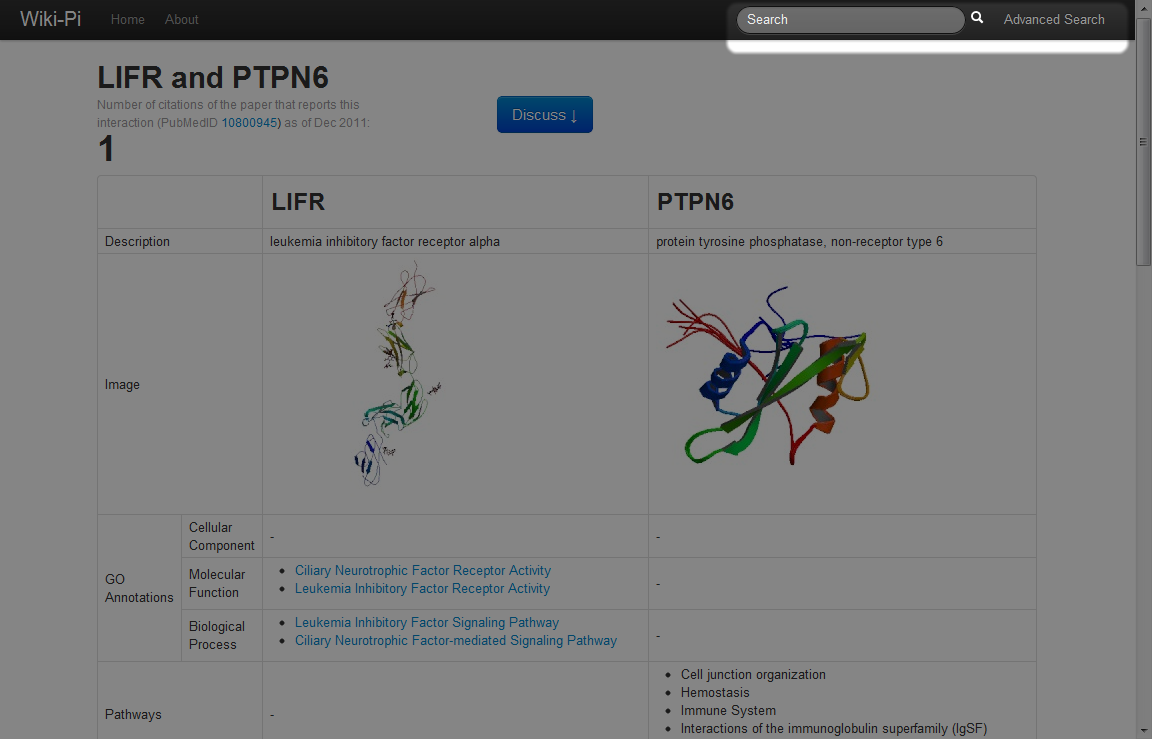
Advanced Search
Protein-protein interactions matching specific conditions can be searched using the Advanced Search functionality. For example, if you want to search for an interaction where "one gene is involved with breast cancer, while the other gene is involved with apoptosis and is NOT invovled with the immune system pathway," you should enter the form as below:
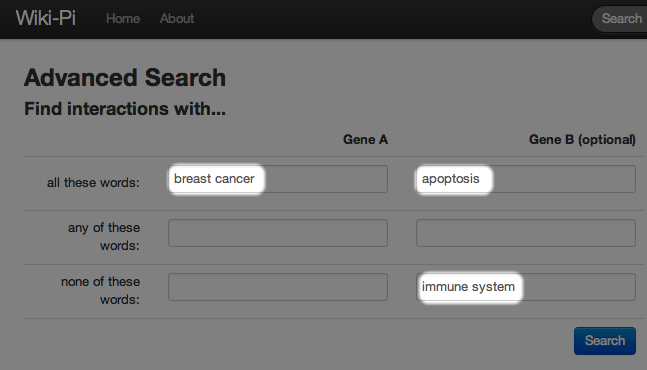
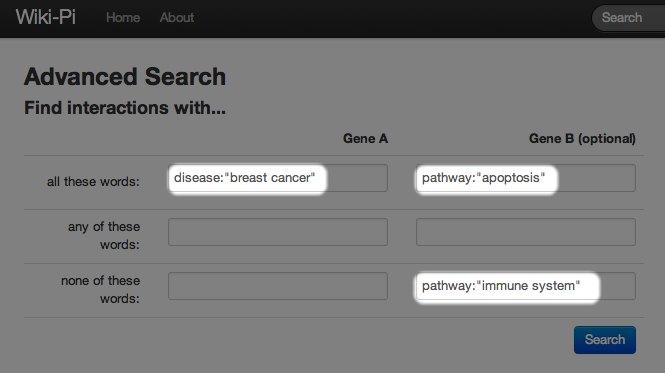
Sometimes your query may have too many search results. In this case, you can specify what your query matches against by using the syntax "field:query". In the previous example, we might want to limit breast cancer to match against diseases, apoptosis to match against pathways, and immune system to also match against pathways. In this case, you should enter the form as below:
Fields you can search against are:- eid (Entrez ID)
- symbol (Gene symbol)
- name (Gene name)
- go (associated GO terms)
- pathway (associated pathways)
- disease (associated diseases)
- drug (binding drugs)
You can also search for interactions of a list of genes. For example, if you are interested in interactions involving genes that are related with the epidermal growth factors (such as EGFR, EPS8, and EGFR), you can should enter the form as follows:
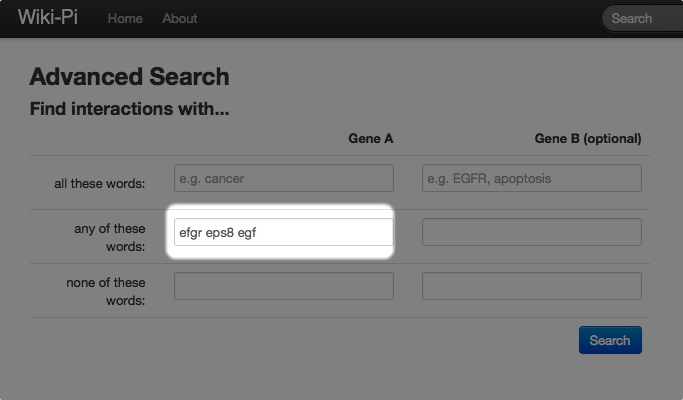
Interaction Page
Each interaction page consists of two sections:
- Automatically updated annotations about the two proteins
- User modifiable content
